| Problem |
Lessons learned are collected in projects but not shared at the organizational level. The same problems are occurring again and again in different projects. |
| Initial Context | An organization has Established an Experience Base (KSP16). Lessons are discovered (KSP15) in project teams. |
| Roles | An organization represented by persons responsible for the maintenance of the experience base. If the experience base is automated enough it could also represent here the organization role. Project manager (including other project team members). |
| Forces | In organizations gained knowledge is "wasted" if not shared. The existing knowledge should not be difficult to find and reuse for e.g. project managers. (Komi-Sirviö et al. 2002.)
Rus and Lindvall (2002) remind of the importance of knowledge sharing in utilizing the individual knowledge at the organization. They say that: ”Large organizations cannot rely on informal sharing of employees’ personal knowledge. Individual knowledge must be shared and leveraged at project and organization levels.” (Rus and Lindvall 2002, p. 27). One important part of the organization level knowledge sharing is the lessons learned type of knowledge. |
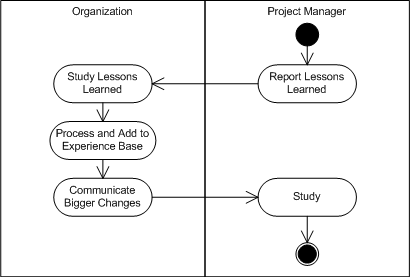
| Solution |
|
| Resulting Context | An organization having implemented systematic experience collecting and storing. |
| Instances | Follow this pattern always when receiving lessons learned of relevant feedback related to the experience base or other such assets.
One potential pitfall is that the lessons learned could be collected and even stored into the system, but in such a way that the system can not be used for retrieving knowledge in a reasonable way. |
| Process Connection | Supports process improvement and organizational development. This can affect any of the processes. |