| Problem | Lessons learned are collected in projects but the organization does not have any systematic way to store and share those to support the work in projects. |
| Initial Context | An organization not having a systematic procedure and environment to collect and share experiences (lessons learned). |
| Roles | An organization represented by by competence or quality management, for example. Project manager (including other project team members). |
| Forces | In organizations gained knowledge is "wasted" if not shared. The existing knowledge should not be difficult to find and reuse for project managers. (Komi-Sirviö et al. 2002.)
Many organizations start their knowledge sharing project by establishing a new database and just assuming, that people will use it when it is ready. But neither contributions nor retrievals occur with much enthusiasm. (Dixon, 2000, p. 2.) Sharing knowledge takes time and effort from e.g. new knowledge development, but on the other hand, exploiting existing knowledge produces enormous cost savings (Dixon, 2000, pp. 19-20). |
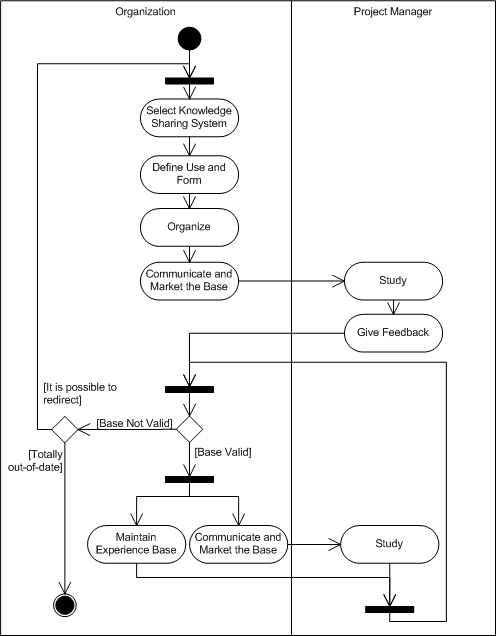
| Solution |
If the experience base is not valid, but through reasonable actions it could be redirected to support the work, a revision and reinitiation could be made. |
| Resulting Context | An organization having initiated an environment for systematic experience sharing. |
| Instances | Establish once, maintain and support with communication continuously.
One potential pitfall is that the project managers and project team members will not see the benefits of this knowledge sharing system and thus not have the motivation to use it. The benefit of the system in practice is thus the most important criterion for the validity of the system. |
| Process Connection | Supports process improvement and organizational development. This can have an affect on any of the processes. |