| Problem | A project manager not knowing the project situation and progress status well enough. |
| Initial Context | A project having a Scheduled Baseline (KSP09). |
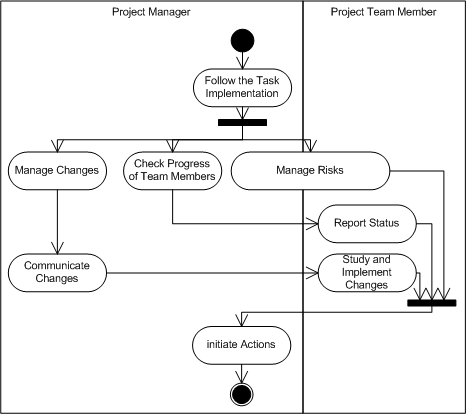
| Roles | A Project Manager managing the project and Project Team Members implementing the project. |
| Forces | Project Manager should constantly know what the real status of a project is compared to project objectives and plans. Without this knowledge, managing a project would be like driving in dense fog.
Well defined tasks create a basis for progress follow-up. If tasks are defined small enough but still have well defined results it is possible to follow progress through the realization of those results. Changes to tasks need to be managed and communicated in a project team. Risk identification allows preventive actions before the identified risk is realized. |
| Solution |
To have adequate work status knowledge the project manager shall:
|
| Resulting Context | A Project Manager running a project where the work status is adequately and continuously known. Risk management is implemented to avoid identified possible problems later. |
| Instances | This is a continuous activity during existing projects. The whole act should be implemented monthly/weekly/daily based on the intensity and criticality of a project.
One potential pitfall is that some engineer reports that the task progresses ok, but that is not the case in practice. See Trust or Check, KSP04 for avoiding such a pitfall. |
| Process Connection | Project Management process, project execution. |