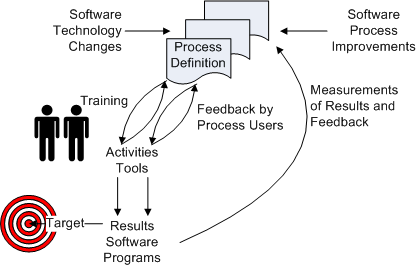
Figure 1. Effective software process environment (modified from Zahran, 1998, p. 68).
| Problem | An organization with a need to establish or improve the guidance of work in the organization in order to allow for more efficient team work. |
| Initial Context | An organization in the software engineering business that has initiated process management. At the project level Shared Understanding (KSP05) exists between the customer and the organization. |
| Roles | An organization represented for example by top management and quality management. A project represented by all project team members. |
| Forces | To guide work in an organization, a communicated and shared target of work is required as well as common processes about how the work should be done. The target guides by showing where to go and the common processes that facilitate team work to achieve the goals.
Aspects of a process (Zahran, 1998, p. 6-7):
According to Zahran (1998, p. 41, see also the Figure 1) the following factors increase process effectiveness:
|
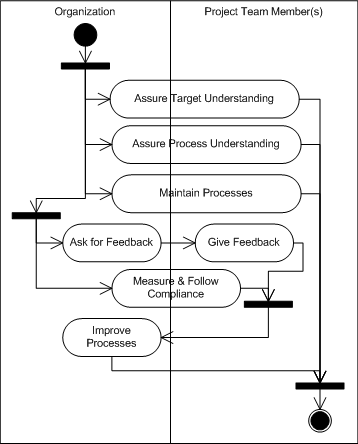
| Solution |
This is a continuous procedure, so when the closing point has been reached it must be restarted. |
| Resulting Context | An organization having well established process management and target understanding. |
| Instances | To initiate the guidance in an organization and to maintain and improve it continuously.
One potential pitfall is to improve and maintain the processes fully separated from the real work resulting in processes that are not reasonable to follow in real life. |
| Process Connection | Business Management and Process Management. |